Maintaining low blood sugar levels can be difficult for diabetic patients.
While a low carb diet appears to be useful on the whole, there are also many foods shown to help. Either by lowering blood sugars and/or improving insulin sensitivity.
This articles looks at 10 of the best foods and supplements for lowering blood sugars, based on current research.
Just know they should never be used in place of your diabetes medication, but rather alongside.
1. Resistant Starch Lowers Sugars After Meals
 Starches are long chains of glucose (sugar) found in oats, grains, bananas, potatoes and various other foods.
Starches are long chains of glucose (sugar) found in oats, grains, bananas, potatoes and various other foods.Some varieties pass through digestion unchanged and are not absorbed as sugar into the blood. These are known as resistant starch.
Many studies show resistant starch can greatly improve insulin sensitivity. That is, how well the body can move sugar out of the blood and into cells for energy.
This is why it’s so useful for lowering blood sugar levels after meals (1, 2).
The effect is so great that having resistant starch at lunch will reduce blood sugar spikes at dinner, known as the “second meal effect” (3).
Problem is many foods high in resistant starch, such as potatoes, are also high in digestible carbs that can spike blood sugar. Therefore resistant starch in supplement form – without the extra carbs – is recommended.
Summary: Supplemental resistant starch is a fantastic option for those struggling to control sugars or have hit a plateau.
2. Ceylon Cinnamon
 Cinnamon has been used for its medicinal properties since Ancient Egypt and China.
Cinnamon has been used for its medicinal properties since Ancient Egypt and China.Several cinnamon compounds appear to prevent the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, minimising blood sugar spikes. It may also dramatically improve insulin sensitivity (4, 5).
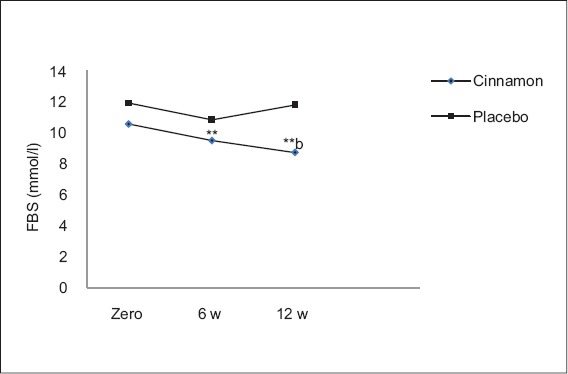
In a recent clinical trial, 25 poorly-controlled type 2 diabetics received either 1 gram per day of cinnamon or placebo (dummy supplement) for 12 weeks.
Fasting blood sugar levels in the cinnamon group dropped by 10% after 6 weeks and 17% after 12 weeks compared to placebo (6).
 Effect of 1 g cinnamon powder on fasting blood glucose. **Highly significant difference from baseline (P < 0.001).
Effect of 1 g cinnamon powder on fasting blood glucose. **Highly significant difference from baseline (P < 0.001).The HbA1c (3-month marker of blood sugar levels) also began to decrease by 8% after 12 weeks, although it did not reach statistical significance.
Note that not all clinical trials have found cinnamon to be effective, so it’s by no means a “miracle” treatment (7).
The recommended dose is 1-6 grams daily, from ceylon rather than cassia.
0 comments:
Post a Comment